Data migration in the days of paper filing systems was a physically strenuous but relatively simple proposition, a matter of transferring records from one location to another. It’s different in the age of big data. Transferring your valuable data from one server or repository to a target system might seem similarly straightforward, but the diversity of data in the 21st century makes the process more complicated than it looks at first glance. To get the job done while preserving the security and integrity of your data, you need a data migration strategy.
Here, we’ll look at the key steps in a cloud migration process for a modern business, focused on the data migration tools you’ll need and the best ways to preserve your data quality as you move resources from a source system — or a series of legacy systems — to your new target systems.
An In-depth look at What Data Migration Is
Data migration is the process of transferring data from one system to another. The data can be transferred in its entirety, or in parts, depending on the needs of the organization. There are a number of factors that need to be considered when planning a data migration, including the source and destination systems, the type of data being migrated, and the timeframe for the migration.
Data migration can be a complex and daunting task, but with careful planning and execution, it can be a successful way to move data from one system to another. By understanding the different types of data migration and knowing the factors to consider when planning a migration, you can ensure that your data migration goes smoothly and without interruption.
Data Migration Strategies and Why You Need it
Simply put, data migration occurs when your company needs to move data from one system to another. It’s basically what needs to happen when your business is looking to introduce new systems and applications and needs to transfer your existing data from your legacy system into a new setting. Understanding data migration and the potential intricacies it involves will help you avoid data loss during this process, taking advantage of data migration software and specialists and leveraging backup strategies for your resources to your advantage.
There are several types of data migration, and it’s important to understand them in order to keep your business processes up and running efficiently throughout the entire process.
- Database migration is the process of migrating your databases to take advantage of more advanced data management, improved performance or cost-effective scaling.
- Storage migration becomes necessary when upgrading your storage technology or switching from on-premises data storage to a cloud solution.
- Application migration is about moving data between app platforms or vendor ecosystems to take advantage of new opportunities.
Without a structured data migration strategy, you could find that even with a seemingly sound base of source data, you might wind up with redundancies and uncertainties in the new data set. Issues that had gone unnoticed in the source data can become amplified in the migrated data, leading to missed deadlines, budget overruns or even the migration project’s overall failure.
Ingredients of a Successful Data Migration Project
Delivering a successful data migration projection means having a structured approach and a dedicated team that can give the task their full attention. There are a few key ingredients that go into making this work.
Data Migration Team
The whole process depends on bringing the right people to your data migration team and giving them the space and time to carry out the process. Both business users and IT staff and consultants should be involved, and the data migration should be its own independent priority for them, not a subordinate part of some larger project. A consistent team should work together across the entire process, and everyone should have access to an easy-to-use data migration software solution.
Data Audit
A thorough data audit is a necessity before you get started. This will alert you to any possible issues in the source data before it becomes an issue and make sure that the data integrity is intact.
Data Cleanup
Any problems the audit uncovers with inaccurate data or other data quality issues will need to be cleaned up before proceeding. Additional data migration tools and third-party resources might be necessary, depending on the scale of the job.
Data Protection
Your important data will tend to degrade over time unless you have controls in place to maintain optimal data quality.
Data Governance
Use automated and user-friendly tools and processes to track and report on the migration process to ensure data quality and integrity.
In order to achieve these outcomes, you need to decide what type of data migration you’ll be using and consider a few key steps.

Deciding on the Type of Data Migration
There are two major approaches to data migration: the big bang project and trickle migration.
Big Bang Data Migration
A big bang migration assigns a specific window of time for transferring data. It involves downtime while the data is processed and transitioned. This presents the attraction of compressing the entire process into a single event but can also involve intense pressure, the more so the longer the downtime lasts. It’s often advisable to rehearse this kind of process before attempting the real thing.
Trickle Data Migration
The legacy system and the new system run in parallel, as a trickle migration happens in phases. This type of migration is designed to keep your business processes up and running and uninterrupted throughout the process while your data is migrated. Planning a trickle migration can be complex, but it pays dividends in the form of reduced risk.
The Key Steps of Data Migration
The key steps in a data migration strategy are planning, preparation, design, execution, testing and maintenance.
- Planning is about assessing the scope of the proposed project, choosing the type of migration and selecting a team, planning the retirement of the legacy system and choosing any software tools you might need.
- Preparation involves auditing the source data, backing it up before the migration process starts — having comprehensive backups is extremely important — and establishing who has rights to access, edit and remove data from the legacy system and to work directly on the target system.
- Design means mapping out the specifics of the migration and which fields and file types in the legacy system will end up in which locations on the target system.
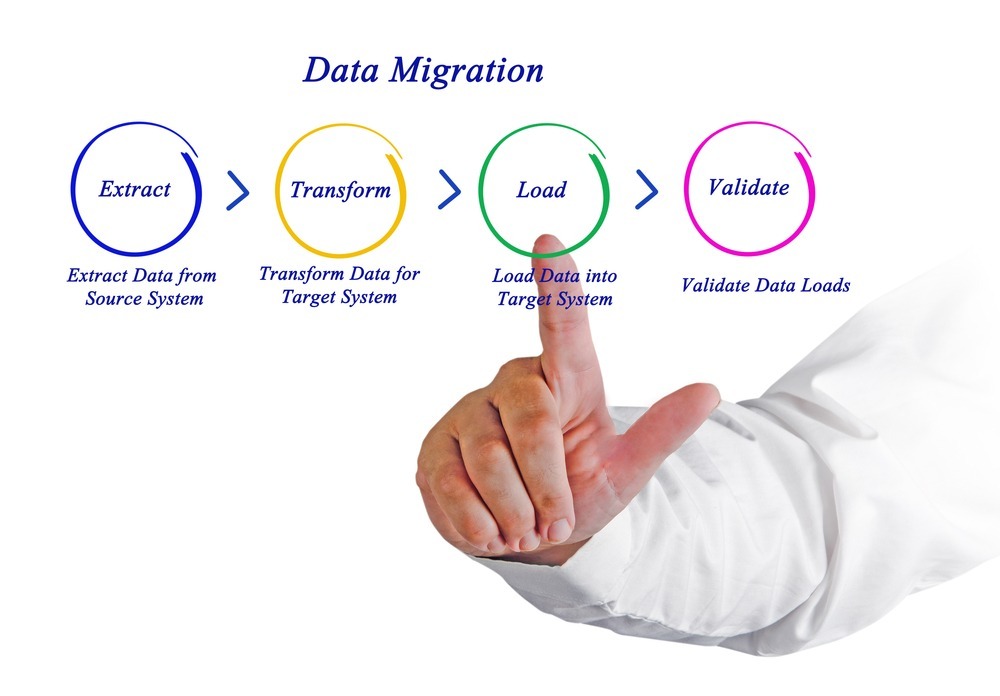
- Execution is the process of extracting the data, transforming it into the correct formats if needed and loading it into the target system. This may involve a rehearsal phase in the case of a big bang project.
- Testing involves testing out each batch of transferred data in a trickle migration or testing the entire transferred data set in a big bang migration, spotting and fixing any issues discovered and then testing again until all stakeholders are satisfied before going live.
- Maintenance is about completing a post-migration audit and monitoring the new system to ensure it’s performing up to expectations.
Things to Consider When Choosing a Software for Data Migration
When it comes to data migration, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is which software to use. But with so many options available, how do you choose? Here are four factors to consider:
1. Ease of use
The software should be easy to learn and use, even for someone who is not familiar with data migration procedures. This will make the process much smoother and less complicated for everyone involved.
2. Compatibility
The software should be compatible with a variety of platforms and systems, so it can be used in different environments. This will ensure that the data can be transferred to the new system with minimal disruption.
3. Scalability
The software should be able to handle large data sets and be scalable for future needs. This is important when doing data migrations as the amount of data can quickly grow beyond what was initially planned. The software should be able to easily adapt and grow with the size of the migration project.
4. Support
When you’re choosing a software vendor for data migration, it’s important to consider the level of customer support they offer. That means you need to be sure the vendor has a good reputation for providing quality customer service, and that they have a team of experts who can help you if you run into any problems.
When it comes to data migration, making the right decision about software is critical. The four factors listed above are important considerations when making your choice. Make sure to choose software that is easy to use, compatible with your current system and the target system, scalable for future needs, and backed by good customer support. By taking into account each of these factors, you can be sure to make the best decision for your data migration needs.

Cloud Migration
A data migration project is a complex undertaking, but migrating data to the cloud can offer many benefits. When planning a data migration to the cloud, it’s important to consider the following factors:
Data type and volume
Not all data is suitable for migration to the cloud. Make sure you understand the data you need to migrate.
Data analysis
Assess what needs to be migrated and how it aligns with your business goals.
Cost
Migrating data can be costly. Be sure to consider the total cost of ownership, including storage, bandwidth, and computers.
Risk assessment
Understand the risks involved in migrating data and put a plan in place to mitigate those risks.
Gaining buy-in from stakeholders
Data migration can be a disruptive process. Be sure to get buy-in from all stakeholders before starting the project.
Once you’ve considered these factors, you can begin to develop a data migration plan. The first step is to assess your current environment and understand how your data is being used. This will help you identify which data should be migrated and how it should be migrated.
Get the Help You Need
Creating and executing a successful data migration strategy is best done in consultation with data experts like the team at EIRE Systems. Contact us today and discover how we can optimize data migration processes and make your business agile and competitive in a fast-moving modern marketplace.
About the Author: EIRE Systems
EIRE Systems is a leading independent provider of professional IT, AV and Access Security services to the financial, insurance, manufacturing, health care, retail, construction, hospitality, commercial real estate, legal, educational and multinational sectors in Japan and throughout the Asia Pacific region. EIRE Systems has expertise across a wide spectrum of Information Technologies, with a track record for successfully completing hundreds of assignments since its establishment in 1996.



